The AI Scaling Lie: Why Google's 'Agent Science' Proves Small Teams Are Already Obsolete

Google Research just unveiled the science of scaling AI agents. The unspoken truth? This isn't about better chatbots; it's about centralizing control and crushing independent AI development.
Key Takeaways
- •Google's research defines the critical 'phase transitions' necessary for large agent systems to work, locking this knowledge behind massive compute resources.
- •The focus shifts from model capability to system coordination science, which favors incumbents with vast infrastructure.
- •This development signals a massive centralization of AI power, making it harder for small teams to compete in complex, reliable agent deployment.
- •Reliability in complex tasks will soon demand proprietary scaling validation only available from hyperscalers.
The AI Scaling Lie: Why Google's 'Agent Science' Proves Small Teams Are Already Obsolete
Stop celebrating the latest multimodal model release. The real earthquake just hit Silicon Valley, and it's not about better image generation; it's about **the science of scaling agent systems**. Google Research has quietly published foundational work detailing precisely *when* and *why* large clusters of autonomous AI agents succeed or fail. This isn't just academic curiosity; it is the blueprint for the next industrial revolution, and it spells doom for anyone not backed by hyperscale infrastructure. If you thought building powerful AI was about clever prompt engineering, think again. It’s about compute density and coordination science. ### The Hard Truth: Performance Isn't Linear, It's Systemic For years, the narrative around AI innovation has been the scrappy startup versus the tech behemoth. We celebrated open-source models as the great equalizer. Google’s new findings fundamentally demolish this premise. Their research shows that task performance in complex, multi-agent environments doesn't scale smoothly with the number of agents or the size of the underlying LLM; it hits critical phase transitions based on system architecture and communication overhead. **The unsung hero here is coordination.** When agents are too few, they fail due to insufficient specialization. When they are too many, they collapse under the weight of communication latency and redundant effort. Google has mapped the 'Goldilocks Zone' for agent swarm effectiveness. Who owns the map? The entities that control the massive compute clusters required to *test* these scaling laws—namely, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon. This isn't research for the public good; it’s proprietary knowledge for building unbeatable economic monopolies. The independent developer is now fundamentally unable to replicate the necessary experimentation to compete at this systemic level. This is the new moat, deeper than any algorithm. ### The Hidden Agenda: Centralization, Not Democratization Why does this matter beyond technical benchmarks? Because the future of work—from complex software development to scientific discovery—will be run by these agent systems. If the foundational *science* governing how these systems reliably scale is locked behind the walls of a few trillion-dollar companies, then those companies control the throttle on global productivity gains. We are witnessing the **centralization of intelligence infrastructure**. The ability to deploy reliable, large-scale agent teams—what Google calls 'Reliability' and 'Performance' in their charts—is directly correlated with access to massive, curated datasets and petascale clusters. Smaller players will be relegated to running low-stakes, easily replicable tasks on top of the foundation models provided by the giants. They become tenants, not landlords, in the new AI economy. This shift guarantees that the economic benefits of advanced AI will accrue disproportionately to the incumbents who funded the very **AI scaling** research that proved their dominance. ### Where Do We Go From Here? The Prediction My bold prediction is that within 18 months, we will see the first major enterprise task—think high-frequency trading algorithms or complex pharmaceutical discovery pipelines—that *cannot* be safely or reliably run by any system outside of a dedicated, internally validated hyperscale agent framework like the one Google is pioneering. Open-source models will remain excellent for creative or simple tasks, but for mission-critical, complex operations, the market will demand the proven, scientifically validated reliability of the walled gardens. The focus will shift from 'Can we build an agent?' to 'Can we *prove* this agent scales reliably?' And only the hyperscalers can prove that. For the rest of us, the only path forward is to become expert *integrators* and *auditors* of these massive systems, rather than primary builders. The age of the lone AI genius is over; welcome to the era of the AI infrastructure consortium. This is a profound moment for **artificial intelligence research**.Gallery
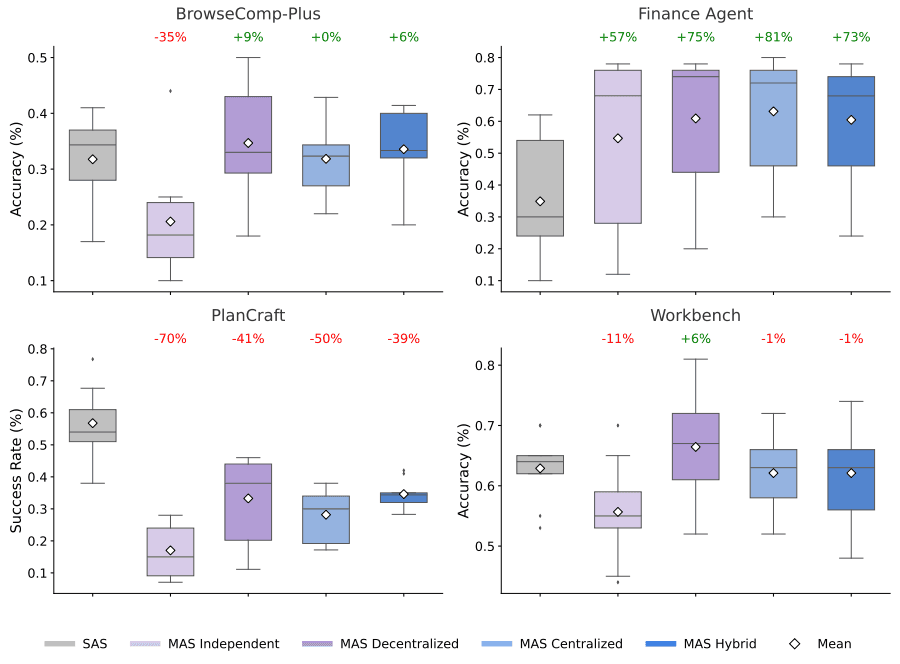

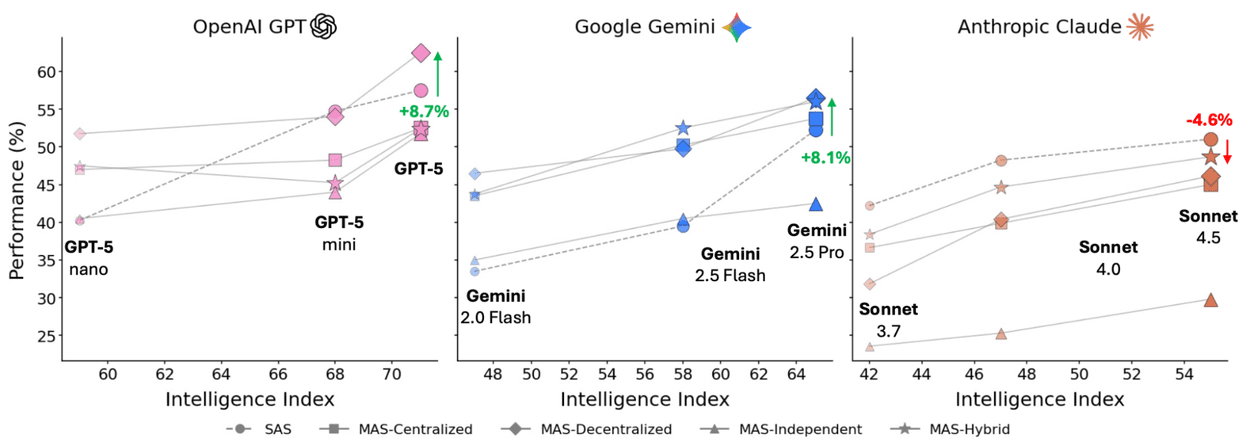
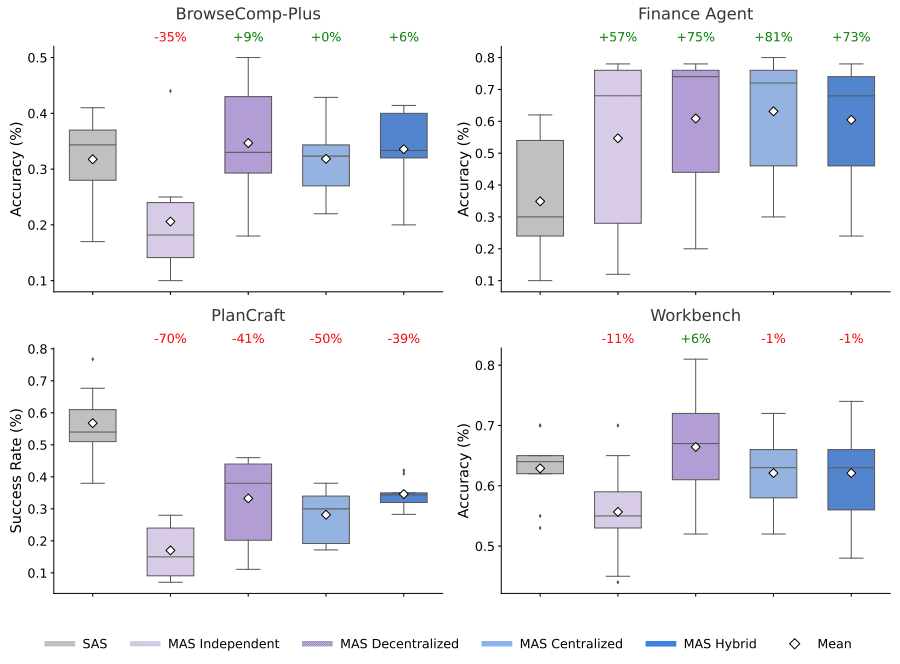
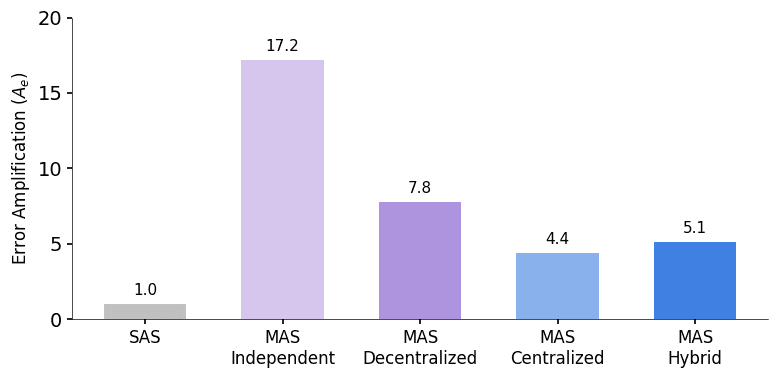


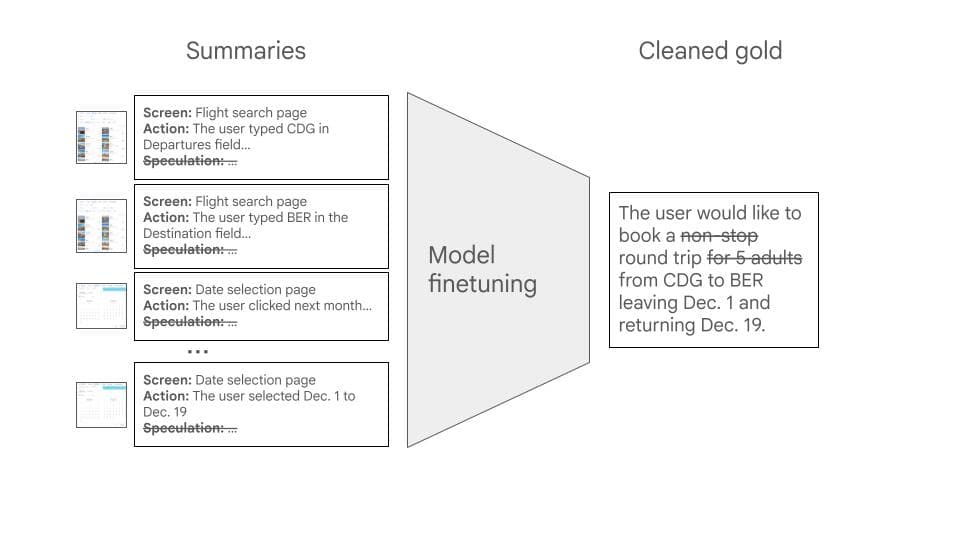
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the 'science of scaling agent systems'?
It is the study and empirical mapping of how the performance and reliability of large groups of autonomous AI agents change as the number of agents and system complexity increases. It seeks to find the non-linear tipping points where systems either dramatically improve or completely fail.
Why is this research considered 'contrarian' or a 'lie'?
The research is framed as democratizing AI, but the complexity involved in testing these scaling laws requires resources only available to major tech giants. Therefore, it serves to solidify their competitive advantage rather than leveling the playing field for smaller developers.
How does this impact small AI startups?
It forces them out of the realm of building core, mission-critical systems. They will likely pivot to using the established, proven scaling frameworks provided by the hyperscalers, turning them into dependent users rather than independent innovators.
What is the difference between scaling LLMs and scaling agent systems?
Scaling LLMs often involves making the model larger (more parameters). Scaling agent systems involves managing the communication, coordination, and task division among *many* independent, specialized AI entities, which introduces complex overhead challenges.
Related News

The 'Third Hand' Lie: Why This New Farm Tech Is Actually About Data Control, Not Just Sterilization
Forget the surface-level hype. This seemingly simple needle steriliser is the canary in the coal mine for agricultural technology adoption and data privacy.

Evolv's Earnings Whisper: Why the Q4 'Report' is Actually a Smoke Screen for a Security Reckoning
Evolv Technology's upcoming Q4 results aren't about revenue; they signal a massive pivot in the AI security landscape. The real story of **advanced security technology** is hidden.

The Media's Quiet Collapse: Why 2026 Tech Predictions Signal the End of 'News' as We Know It
Forget AI hype. The real threat revealed in 2026 media tech trends is the death of shared reality. Are you ready for hyper-personalized echo chambers?

DailyWorld Editorial
AI-Assisted, Human-Reviewed
Reviewed By
DailyWorld Editorial